

I am Ningke Li, a first-year CS Ph.D. student at the TEST Lab, National University of Singapore, where I have been conducting research under the supervision of Prof. Manuel Rigger since 2025. My research focuses on improving the reliability of complex systems through two primary directions: leveraging AI techniques to enhance software testing (AI for Testing) and systematically evaluating and strengthening the trustworthiness of AI systems (Testing for AI). I also have experience in program analysis and source code vulnerability detection.
I received my master degree in Cybersecurity from Huazhong University of Science and Technology in 2025 under the supervision of Prof. Haoyu Wang and Prof. Kailong Wang. I received my B.E. degree in Information Security from Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications in 2022.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "👩🎓Education
-
National University of Singapore
 TEST Lab
TEST Lab
Ph.D. StudentAug. 2025 - present -
Huazhong University of Science and Technology
 Security Pride Lab
Security Pride Lab
M.S. in CybersecuritySep. 2022 - Jun. 2025 -
Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications
 B.S. in Information SecuritySep. 2018 - Jun. 2022
B.S. in Information SecuritySep. 2018 - Jun. 2022
🏆 Honors & Awards
-
China National Scholarship2023
-
Outstanding Graduates of Beijing2022
-
China National Scholarship2019
👩🏻🏫 Services
-
Reviewer/Sub-reviewerASE, FSE, MSR, Internetware, EMSE, ICECCS...
-
Student VolunteerOOPSLA 2025
-
MemberNUS SoC Student Area Search Committees
News
 Recent Publications
(view all )
Recent Publications
(view all )
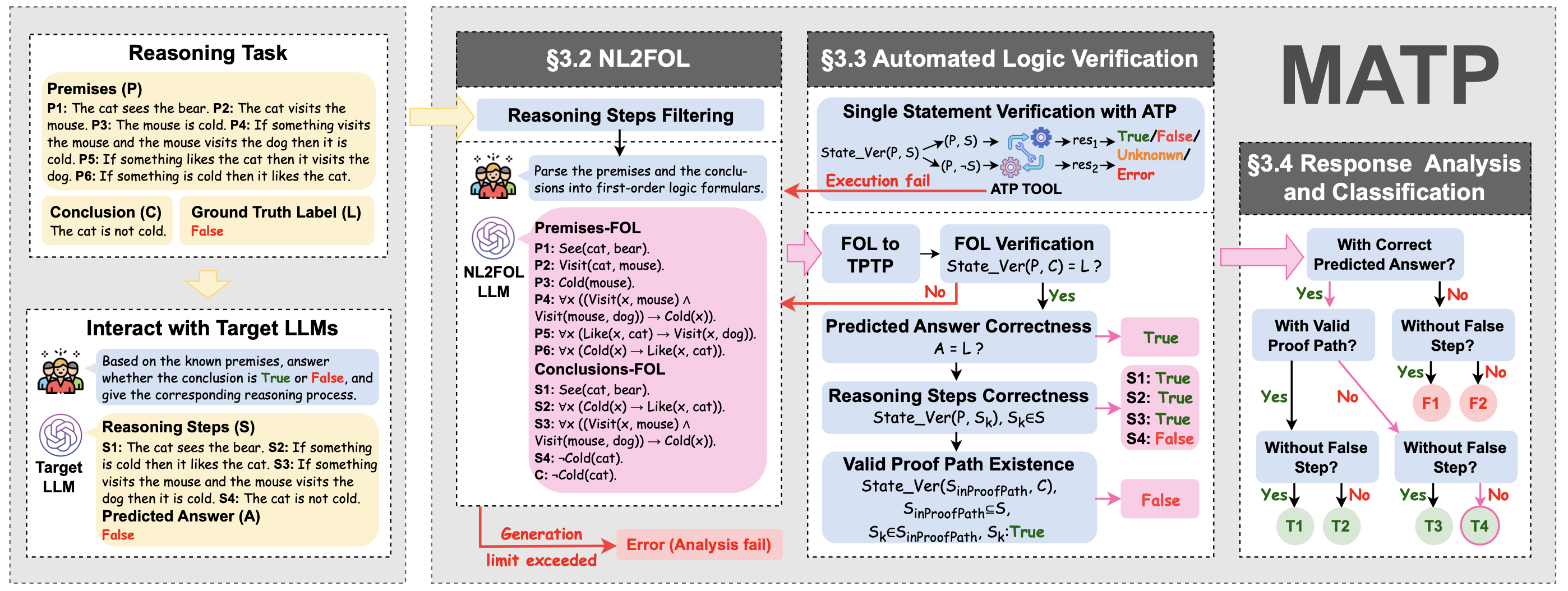
Beyond Correctness: Exposing LLM-generated Logical Flaws in Reasoning via Multi-step Automated Theorem Proving
Xinyi Zheng*; Ningke Li*; Xiaokun Luan; Kailong Wang; Ling Shi; Meng Sun; Haoyu Wang. (* equal contribution)
48th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE) 2026
An automated theorem-proving-based framework for verifying multi-step LLM reasoning, translating natural language into first-order logic to detect hidden logical errors and systematically assess reasoning correctness across diverse benchmarks.
Beyond Correctness: Exposing LLM-generated Logical Flaws in Reasoning via Multi-step Automated Theorem Proving
Xinyi Zheng*; Ningke Li*; Xiaokun Luan; Kailong Wang; Ling Shi; Meng Sun; Haoyu Wang. (* equal contribution)
48th IEEE/ACM International Conference on Software Engineering (ICSE) 2026
An automated theorem-proving-based framework for verifying multi-step LLM reasoning, translating natural language into first-order logic to detect hidden logical errors and systematically assess reasoning correctness across diverse benchmarks.
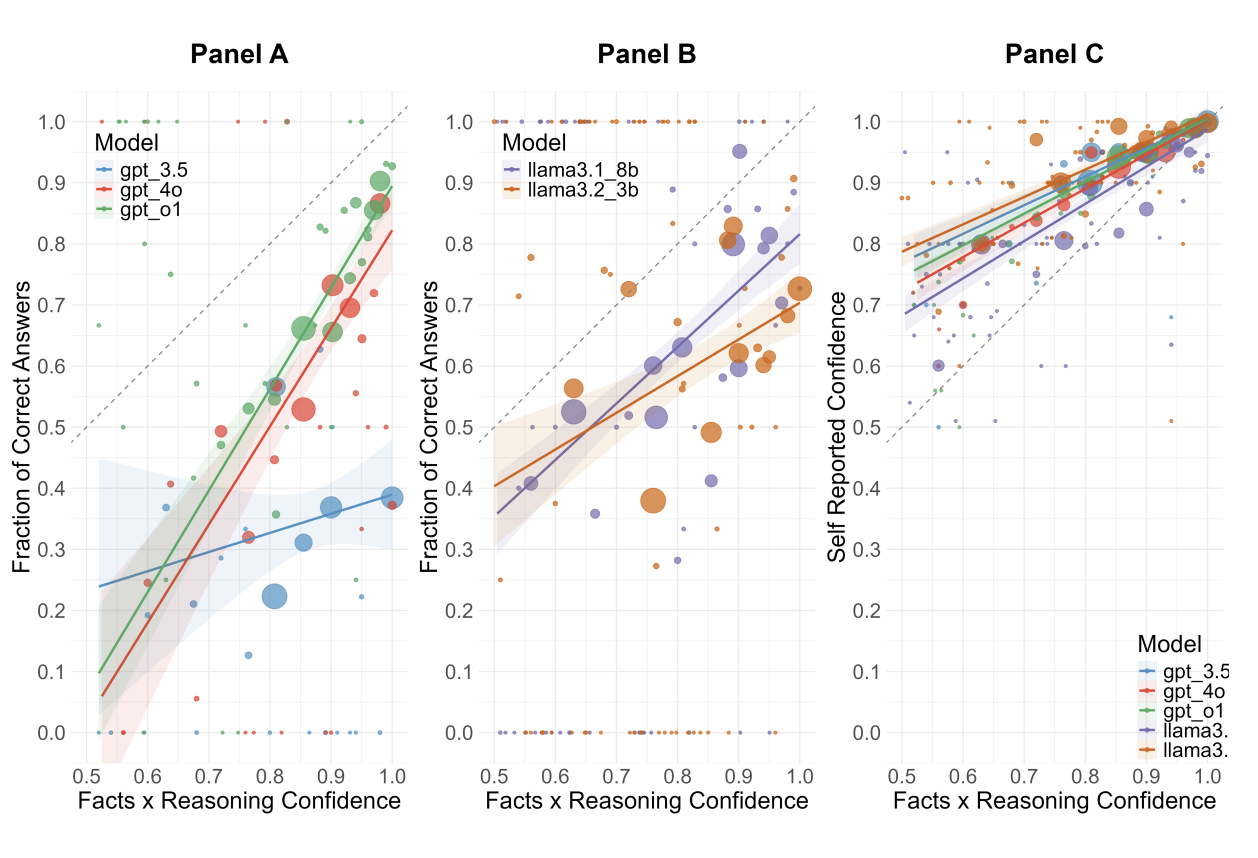
Large Language Models are overconfident and amplify human bias
Fengfei Sun*; Ningke Li*; Kailong Wang; Lorenz Goette. (* equal contribution)
Under review 2025
LLMs exhibit significant overconfidence in reasoning tasks, often exceeding human levels, and can amplify human overconfidence when their outputs are used as input.
Large Language Models are overconfident and amplify human bias
Fengfei Sun*; Ningke Li*; Kailong Wang; Lorenz Goette. (* equal contribution)
Under review 2025
LLMs exhibit significant overconfidence in reasoning tasks, often exceeding human levels, and can amplify human overconfidence when their outputs are used as input.
Large language models for cyber security: A systematic literature review
Hanxiang Xu; Shenao Wang; Ningke Li; Kailong Wang; Yanjie Zhao; Kai Chen; Ting Yu; Yang Liu; Haoyu Wang.
ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology (TOSEM) 2025
A literature review about the use of LLMs in cybersecurity, analyzing applications, trends, techniques, and challenges.
Large language models for cyber security: A systematic literature review
Hanxiang Xu; Shenao Wang; Ningke Li; Kailong Wang; Yanjie Zhao; Kai Chen; Ting Yu; Yang Liu; Haoyu Wang.
ACM Transactions on Software Engineering and Methodology (TOSEM) 2025
A literature review about the use of LLMs in cybersecurity, analyzing applications, trends, techniques, and challenges.

Drowzee: Metamorphic Testing for Fact-conflicting Hallucination Detection in Large Language Models
Ningke Li*; Yuekang Li*; Yi Liu; Ling Shi; Kailong Wang; Haoyu Wang. (* equal contribution)
Object-Oriented Programming, Systems, Languages & Applications (OOPSLA) 2024
Fact-Conflicting Hallucinations in LLMs are prevalent and challenging to detect, but logic-programming-based metamorphic testing effectively generates diverse test cases and identifies reasoning errors across multiple models and domains.
Drowzee: Metamorphic Testing for Fact-conflicting Hallucination Detection in Large Language Models
Ningke Li*; Yuekang Li*; Yi Liu; Ling Shi; Kailong Wang; Haoyu Wang. (* equal contribution)
Object-Oriented Programming, Systems, Languages & Applications (OOPSLA) 2024
Fact-Conflicting Hallucinations in LLMs are prevalent and challenging to detect, but logic-programming-based metamorphic testing effectively generates diverse test cases and identifies reasoning errors across multiple models and domains.

